- The uptake from the ships main or auxiliary boilers
- An independent inert gas generator, or
- A gas turbine plant when equipped with an afterburner.
Different types of Inert Gas:
Inert Gas for ship’s can be one of the following gas and the choice of this gasses is depending on the product being carried and the capacity required.
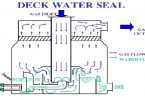
- Inert Gas is generated by burning MDO ( marine diesel oil) in a furnace and the exhaust gas is blown by ordinary blowers via a scrubber/filter unit for cleaning out the sulphur, towards the Cargo tanks; ( This unit making the Inert gas is often called Inert Gas Generator)
- Flue Gas:- This Gas is exhaust gas from the steam generating boilers or occasionally from the main engine and blown by a blower via a scrubber/filter unit for cleaning and cleaning out the sulphur towards the cargo tanks.
- Nitrogen, which is made by blowing compressed air from the booster compressor through a small fibre tube, like a Filter material, or via an absorbtion filtering system, by which the air and its gasses will be separated and finally N2 will be forwarded to the Cargo tank by means of the overpressure caused by the booster compressor.
Nitrogen
- Pressure is up to 11,5 bar depending on installation.
- Gas composite (up to 99,9 % N2)
- Dew point down to minus 70 Celsius.
- This gas can be used for all Cargoes as the purity of the N2 is very hIGh and no water content or Hydrocarbons are present.
- For pipeline stripping a separate pipeline with buffer tank pressurised up to 11 bar can be used.


IG density 1.044t/M3 and Air density at atm pr : 1.22 t/M3 ..how is then iG heavier then air sir..can you confirm or correct me pls
Density of IG is mentioned as 1.044 t/m3 , however the density of air is around 1.22 t/m3 at atm pressure,how is then that IG is heavier then air sir..can you clarify or correct me pls
Hello Sir
what is the inert gas combination and its range in an IG O2 Analyser?