Inert gas means a gas or a mixture of gases, such as flue gas, containing insufficient oxygen to support the combustion of hydrocarbons.
The oxygen content of the Inert Gas supplied to cargo tanks should be 5% or less. However, it is to be noted that too less content of oxygen in the IG would introduce other impurities into the cargo tanks.
After efficient scrubbing of the inert gas, the typical constituents of a flue gas are :
- Nitrogen (N)- 83%
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)- 12-14%
- Oxygen( O2) 2-4%
- Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) 50 ppm
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Trace
- Nitrogen Oxides ( NOx ) 300 ppm
- Water Vapour (H2O) Trace (hIGh, if not effectively dried)
- Ash and Soot C Traces
- Density 1.044 (heavier than air)
Inert condition means a condition in which the oxygen content throughout the atmosphere of a tank has been reduced to 8% or less by volume by addition of inert gas .


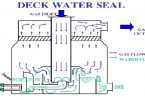
IG density 1.044t/M3 and Air density at atm pr : 1.22 t/M3 ..how is then iG heavier then air sir..can you confirm or correct me pls
Density of IG is mentioned as 1.044 t/m3 , however the density of air is around 1.22 t/m3 at atm pressure,how is then that IG is heavier then air sir..can you clarify or correct me pls
Hello Sir
what is the inert gas combination and its range in an IG O2 Analyser?