Semidiurnal Tide
A semidiurnal tidal pattern has two high tides and two low tides each lunar day. The heights of successive high tides and successive low tides are approximately the same.11 Semidiurnal tides are common along the Atlantic Coast of the United States. The tidal period is 12 hours 25 minutes.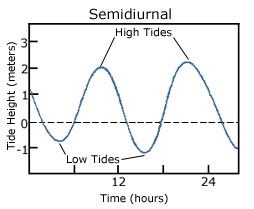
Mixed Tide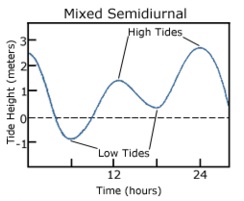
A mixed tidal pattern may have characteristics of both diurnal and semidiurnal tides. Successive high tides and/or low tides will have significantly different heights, a condition called diurnal inequality. Mixed tides commonly have a tidal period of 12 hours 25 minutes, but they may also exhibit diurnal periods. Mixed tides are the most common type in the world, including along the Pacific Coast of North America.
Spring tide :
During the times of new and full Moon. With the Earth, Moon, and Sun lying approximately on the same line, the attractive forces of the Sun are acting in the same direction as the Moon’s attractive forces (modified by declination effects). The resultant tides are called spring tides, whose ranges are greater than average.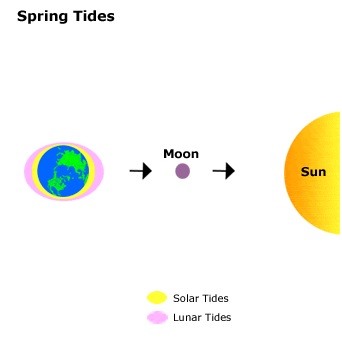
Neap tide :
Between the spring tides, the Moon is at first and third quarters. At those times, the attractive forces of the Sun are acting at approximately right angles to the Moon’s attractive forces. The results are tides called neap tides, whose ranges are less than average.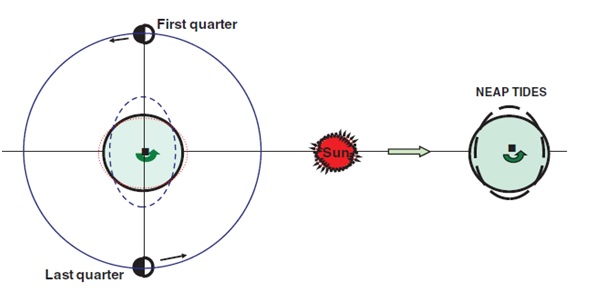
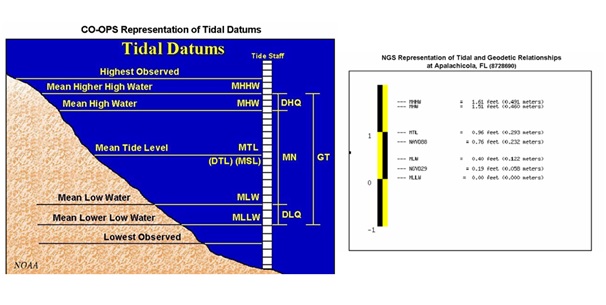
Basics terminology to understand tidal level:
Mean low water (MLW) is the average height of all low waters at a given place. About half of the low waters fall below it, and half above.
Mean low water springs (MLWS), usually shortened to low water springs, is the average level of the low waters that occur at the times of spring tides.
Mean lower low water (MLLW) is the average height of the lower low waters of each tidal day.
Tropic lower low water (TcLLW) is the average height of the lower low waters (or of the single daily low waters if the tide becomes diurnal) that occur when the Moon is near maximum declination and the diurnal effect ismost pronounced. This datum is not in common use as a tidal reference.
Mean lower low water springs (MLLWS) is the average level of the lower of the two low waters on the days of spring tides.
Mean high water springs (MHWS), which is the average level of the high waters that occur at the time of spring tides;
Mean higher high water (MHHW), which is the average height of the higher high waters of each tidal day.
Tropic higher high water (TcHHW), which is the average height of the higher high waters (or the single daily high waters if the tide becomes diurnal) that occur when the Moon is near maximum declination and the diurnal effect is most pronounced.
Approximately, spring tides will be 25% greater than the mean range and neap tides will be 25% less than the mean range.