Different types of Indicator diagrams and their purpose:
i) Power card – To calculate indicated power. It also shows peak pressure. It is taken in phase with piston movement, with fuel on.
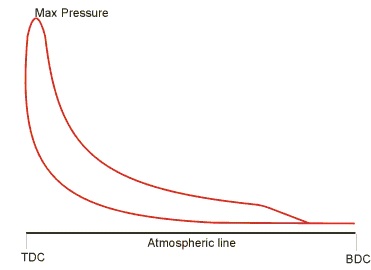
FIG.: POWER CARD
ii) Draw card (90 degrees out of phase)– Similar to power card but taken with the indicator drum rotation 90 degrees out of phase, with fuel on.
It shows Pmax (more accurately), P compression and ignition delay period (Nature of expansion curve). It also shows combustion process (early or late combustion)
To evaluate fuel injection process, ignition delay, fuel quality, combustion, loss of compression, expansion process, fuel pup timing, and after-burning.
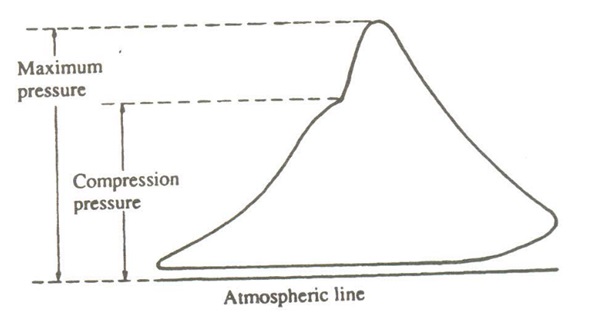
FIG.: DRAW CARD
iii) Compression diagram- It is only a line on the indicator diagram and gives the compression pressure and a timing check on the indicator cam. It is taken in phase with fuel cut-off and at reduced RPM.
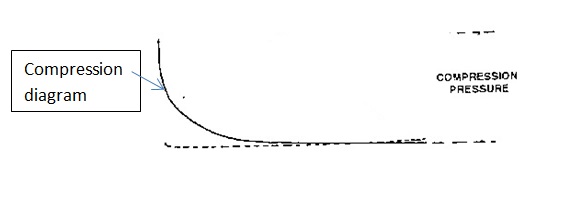
FIG.: COMPRESSION CARD
iv) Light spring diagram – It is taken similar to power card and in phase with engine, but with the light compression spring fitted to the indicator. It shows the pressure variations during the exhaust and scavenging operations.
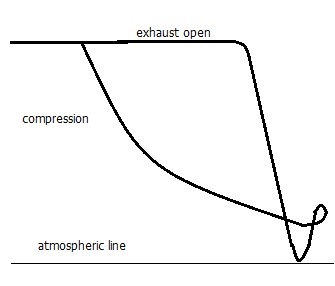
FIG.: LIGHT SPRING DIAGRAM
v) Pressure derivative card- It shows the maximum rate of pressure rise and the point of injection. It is used to highlight ignition delay.


