- Flag States may request information on the location of their vessels around the world
- Coastal States may request information on ships up to 1 000 nautical miles from their coasts irrespective of their flag
- Port States may request information on those ships that have declared one of their ports as destination, irrespective of their location or flag
- Search and rescue authorities.
How does LRIT work?
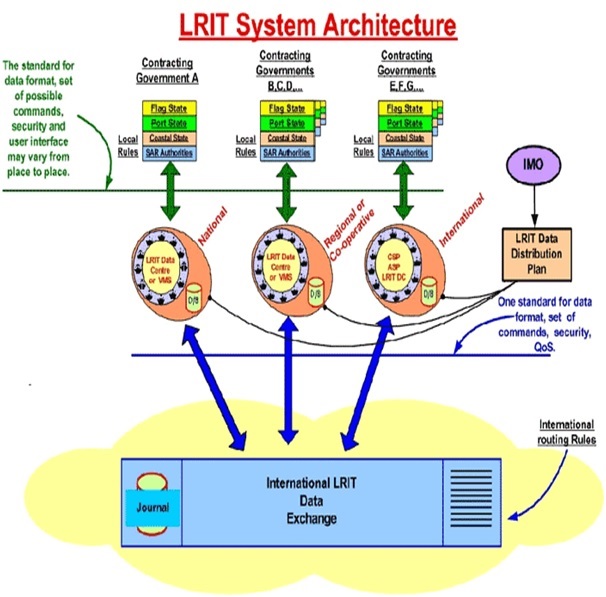
LRIT Shipborne equipment transmits position information to the Communication Service Provider (CSP).
- Communication Service Providers (CSP) provide the communication infrastructure and services to ensure the end-to-end secure transfer of the LRIT message between the ship and ASP.
- Application Service Providers (ASP) provide a communication protocol interface and add information to the LRIT message between the CSP and the LRIT Data Centre.
- LRIT Data Centre collects and provides LRIT information to its users according to the Data Distribution Plan.
LRIT Data Distribution Plan (DDP) defines rules and access rights (i.e. which users can receive what LRIT information). The DDP server is managed by IMO and is populated by SOLAS Contracting Governments, following IMO technical specifications. International LRIT Data Exchange (IDE) routes LRIT information between LRIT Data Centres according to the DDP.
The LRIT regulation will apply to:
To the following ship types engaged on international voyages.