Echo Sounder is a type of SONAR (originally an acronym for SOund Navigation And Ranging) used to determine the depth of water by transmitting sound pulses into water. The time interval between emission and return of a pulse is recorded, which is used to determine the depth of water along with the speed of sound in water at the time.
The History
After the disaster of the Titanic in 1912, the German physicist Alexander Behm conducted some research to find a way to detect icebergs. He discovered the technique of echo sounding which turned out to be inefficient in spotting icebergs, but a great tool to measure the depth of the sea. Behm had his invention patented in 1913. While the first serious attempts to quantify fish biomass were conducted in the 1960’s, major advances in equipment and techniques took place at hydropower dams in the 1980’s. Some evaluations monitored fish passage 24 hours a day for over a year, producing estimates of fish entrainment rates, fish sizes, and spatial and temporal distributions.
Application of echo-sounding principles to submarine detection during World War II resulted in the development of equipment to sound all ocean depths.
In the 1970’s, the dual-beam technique was invented, permitting direct estimation of fish size in-situ via its target strength. The first portable split-beam hydroacoustic system was developed by HTI (Hydroacoustic Technology, Incorporated) in 1991, and provided more accurate and less variable estimates of fish target strength than the dual-beam method. It also permitted tracking of fish in 3D, giving each fish’s swimming path and absolute direction of movement. This feature proved important for evaluations of entrained fish in water diversions as well as for studies of migratory fish in rivers. In the last 35 years, tens of thousands of mobile and fixed-location hydro acoustic evaluations have been conducted worldwide.
What is principle of Echo Sounder operation?
- Echo sounder measures the depth of water by measuring the time for a pulse of energy to travel to the sea bed and back and work on the principle of reflection of acoustic energy.
- Short pulse of sound energy is transmitted vertically down from the ship.
- This pulse having been reflected from the sea bottom returns to the ship in the form of an echo.
- Travel time (t) taken for its return, depends upon the depth of water (d), and on the velocity of sound (v) through the water.
- Time taken (t ) = (2 x d) / v or d =(v x t)/2
- Performance of a sonar system depends on the accuracy with which the velocity of source propagation is measured.
The velocity of propagation is a function of temperature of water, pressure and salinity. The velocity is usually taken as 1500 meters/second for sea water at 13°C and atmospheric pressure.
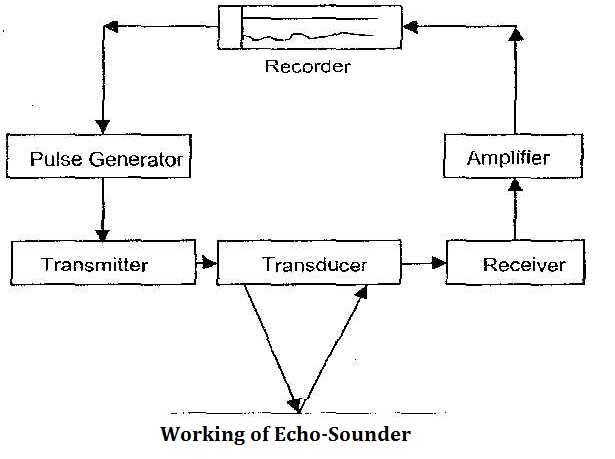
Working of Echo Sounder
- The recorder sends a signal to the pulse generator which triggers a pulse and simultaneously starts the recorder trace.
- The rate may be between 5-600 pulses a minute depending upon the depth to be measured.
- Lesser the depth scale, faster the Pulse Repetition Frequency.
- The pulse from the Pulse Generator activated the transmitter which sends a powerful electric pulse to the Transducer.
- The transducer converts the electric energy into sound energy producing a pulse.
- The sound energy travels to the bottom, hits the bottom and gets reflected back to the transducer.
- The transducer converts the received sound energy of the echo into an electric pulse and sends it to the receiver.
- In the receiver the received pulse is processed and then amplified and sent to the Recorder.
- At the recorder, the stylus which has been at a speed proportional to the speed of sound, creates a physical mark on a paper or a visual blip or a digital signal for the recorder.
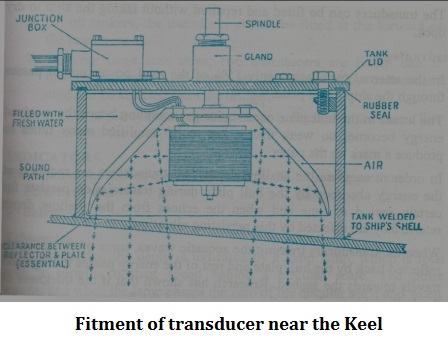
What is Transducer of Echo-Sounder?
- Magneto-Striction is an effect which occurs in all ferromagnetic material, but particularly pronounced in iron, nickel and cobalt.
- These items when placed in a magnetic field change their length.
- Conversely, when subjected to physical stress they generate an emf.
- When alternating current is used to create a magnetic flux, the transducer will vibrate producing a sound pulse.
- Sighting of the Transducer
- Away from noise sources and areas of turbulence like the propeller and discharges.
- Away from aeration which is caused due to bubbles generated by the bow wave or irregularities on the hull, log tubes and discharge orifices.
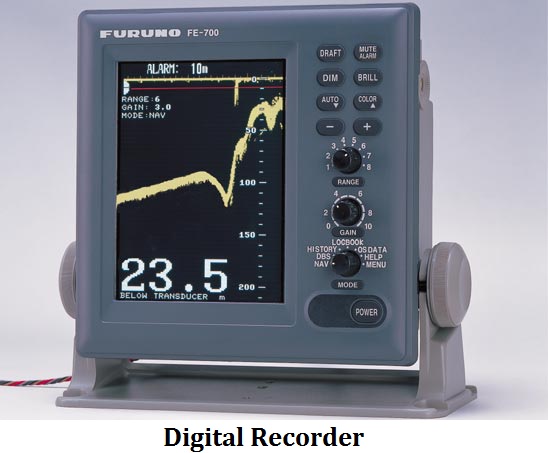
What is Recorder of Echo-Sounder?
- This is the component of the ES a mariner would be using on the bridge.
- Earlier, the echo of the bottom used to be recorded as a mark on paper.
- Currently the old style paper recorder have been replaced by electronic displays showing the bottom echo as blip.
- However, IMO regulations require that a ship must have hard copies of past depth soundings which can only be done on paper.
- A paper recorder consists of a stylus which is made to move across electro-sensitive paper.
- When the transmitter fires its pulse, the stylus marks the paper at the zero of a graduated scale.
- While the pulse travels to the bottom the stylus moves in tandem across the paper but at a speed proportional to half the speed of sound.
- Why half? Because the stylus has to represent the to and fro journey of the transmitted pulse.
- On detection of an echo, the stylus again marks the paper which shows depth of water.
- Even after marking the depth, the stylus will continue traveling towards the end of the paper.
- On reaching the end, the stylus flies back to the zero signifying next transmission and the paper moves down providing a fresh surface for the next echo.
- The process above will be repeated.
- A trace can be seen to be developing on the paper with time on one axis and the echoes on the other building a profile of the sea bottom on paper.
- The speed of the stylus will move depending upon the chosen range scale.

What are the Settings on the Echo Sounder?
Range Switch of Echo sounder
- Could be between 0-10M, 0-20M, 0-50M, 0-100M, 0-200M, 0-1000, etc.
- Check the approximate depth in the vicinity of your fix.
- Start at a range which is just little more than this depth. (if the depth is 98M, choose 0-100M)
- Look out for an echo blip or a marking.
- To coax out the echo, you may have to manipulate other controls.
- Once observed, shift to one range scale higher.
- Observe the echo against the enhanced range scale marking.
- It should be the same as the earlier readings.
Draught Setting of Echo sounder
- The E/S Transducer is fitted at the keel of the ship.
- It means that the depth will be measured below the keel.
- To obtain the depth of water, the draft of the ship will have to be added to the measured reading. This can be achieved by setting this control which is known as setting the Zero Line to the ships draught.
- It is safest to keep the switch to 0 setting because there have been instances when the watch keeper presumed that he was reading below the keel reading whereas the zero line was set to the draft of ship. The watch keeper thus over read the depth and ship ran aground.
Feet / Fathom / Meter Selector Switch of echo sounder
- In modern echo sounders, the display automatically adjusts to the chosen scale.
- If your are on Meter scale and the depth shown is 10M,
- It will show 33ft if the Feet scale is selected.
- Or 5.5 Fathoms if the fathom scale is shown
- But in older models, the marking depth will have to be manually read off against the scale and here caution has to be exercised. There have cases, when watch keeper presumed that the Fathom scale was in use, where the echo sounder was set to Meter Scale.
- The watch keeper presumed higher depth which in reality was lower and hence the ship ran aground.
Fix Marker of Echo sounder
When pressed, it marks the paper. This is done for creating a record as an evidence of a action like a fix or a a happening like a light coming on the beam.
Paper Speed Control (Fast / Slow) of Echo sounder
Faster the paper clear the record trace which is essential to appreciate the shape of the sea bottom. This visual display is a great help when sounding is used to fix a ship.
Gain & Sensitivity of echo sounder
To make echoes darker on the paper. Best set to when the echoes become just about discernible.
Dimmer of echo souder
Keep to optimum settings or else it will affect your night vision.
What are errors of echo sounder?
Velocity Error
- Velocity increases as the salinity, pressure and temperature increases.
- Of these three, salinity setting is the most important followed by the temperature.
- If the velocity reading is less than what it should be, the E/S will under read which though not desirable in not dangerous.
- So if you forget to correct the settings when the ship enters the Red Sea from the Gulf of Aden, the E/S will under read the depth.
- But when you enter Mediterranean later and forget to correct the settings, the E/S will over read the depth and that could be dangerous.
Aeration
- Bubbles are created the keel and the sea bottom due to hard use or rudder, heavy pitching when lightly loaded, breaking water over shoals or rough weather.
- The bubble will absorb the sound energy and no marking will be seen on the E/S or there will be under reading of depth.
- No remedy available, except that these is a temporary condition and will get corrected quickly.
Stylus Speed Error
- The stylus rotates at such a speed the time taken for the stylus to travel from top to bottom is twice the distance of the range selected.
- If the stylus rotates at a different speed (due to voltage fluctuation or sticky tape), the depth recorded will be different.
- Adjustment is made as per instructions given in the manual.
Multiple Echoes
- In shallow water, the sound energy received at the ship after it is reflected from the sea bottom, may get re-reflected from, reach the sea bottom and get re-re-reflected and mark an echo second time over at twice the depth. .
- Or may even an echo third time over at thrice the depth.
- The first echo shows the correct depth. The second and third echoes can be clearly discerned as they grow progressively weaker.
- Something akin to the multiple echoes in Radar.
- Remedy Operate at a scale close to the prevalent depth.
False Bottom Echoes
- This error happens when the range setting is lesser than the prevalent depth.
- The echo arrives at the E/S after the stylus has completed its one trace run and has begun the next trace.
- This will result in considerable under reading.
Pythagoras Error
- This occurs when a ship uses separate transmitters for transmission of the sound pulse and reception of the echo.
- The transmitters are physically separated on either side of the keel or separated along the length of the keel.
- The depth measured at the E/S will be the slanted depth and not the direct below the keel depth.
- In deep waters, this error will not matter much but in shallow waters there will be considerable over reading which is dangerous.
Phased Ranges
- This is a technique to improve the quality of the echo displayed.
- The stylus does not begin its journey when the transmission occurs.
- The stylus starts moving after a delay which is introduced to match the depth of water to be measured.
- This ensures that the stylus is moving when the echo arrives at the E/S.
- For example, if it is intended to measure upto 200 meters of depth with stylus moving for 100 meter depth setting, the stylus begins to move after a time delay equivalent to and fro travel of sound upto 100 meters.
- Advantage of this method is that regardless of the depth of the water, the stylus is made to travel at the same speed meant of a lower depth which gives a clear and uncluttered picture.
- In Edrich Fernandese book, the Setting 1 is for 0-100m depth, Setting 2 is for 100m-200m depth and setting 3 is for 200-300m depth.
Why is Sound Propagation used in echo sounder?
- Sound propagation in water is used in marine navigation, as it is the only form of propagation, which could be, considered as efficient.
- Other forms, e.g. electromagnetic or light radiation attenuates rapidly and is of no use underwater
- Echo sounder, an aid to measure depth of water and Doppler log to measure speed are two sonar devices used in navigation.
Related Searches: