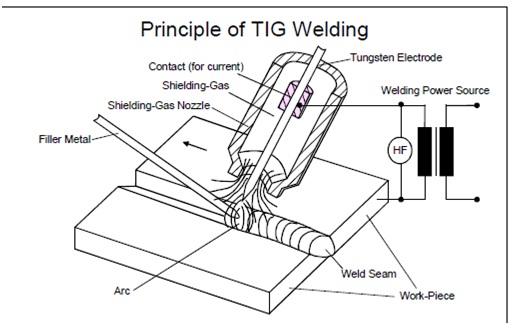
TIG Welding stands for Tungsten Inert Gas and is a technique that’s known for using a non-consumable tungsten electrode along with an inert gas (usually argon). Tungsten is a rare, hard element that offers a high purity, high-quality weld.
In TIG welding, the heat is created by running an electric current through a tungsten electrode, creating an arc that is then used to melt a metal wire in order to create the weld pool.
TIG is most commonly used to weld stainless steel together, although other metals like magnesium, aluminum, copper and nickel can be welded using TIG.
TIG welding is the most widely used fusion welding process for aluminium.
During TIG welding, an arc is maintained between a tungsten electrode and the work piece in an inert atmosphere (Ar, He, or Ar-He mixture).
Depending on the weld preparation and the work-piece thickness, it is possible to work with or without a filler.
The filler can be introduced manually or half mechanically without current or only half mechanically under current.
The process itself can be manual, partly mechanised, fully mechanised or automatic.
The welding power source delivers direct or alternating current (partly with modulated or pulsed current).
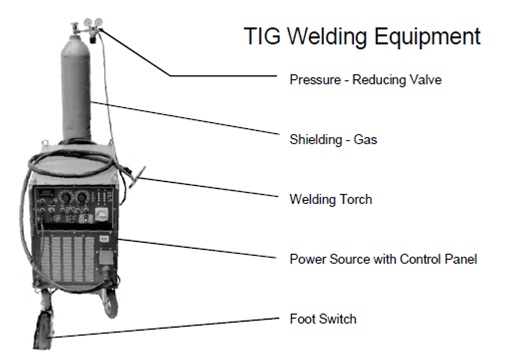

Leave a Comment